This blog provides an overview of Traffic Flow Templates (TFTs) in LTE networks and the EPS network elements involved. TFTs are packet filters that map data flows to appropriate EPS bearers. This enables optimization and prioritization of services to manage quality of experience.
TFTs are important because they allow mapping of data flows to suitable QoS levels. This is essential for handling the increasing demands of high bandwidth applications. We’ll explore what TFTs are, why they matter, and how they operate within the Evolved Packet System. Key concepts around TFT signaling and usage will be covered to help better comprehend their pivotal role in traffic management in LTE networks.
Understanding Traffic Flow Templates (TFTs)
Traffic Flow Templates (TFTs) are packet filters that map different data flows to appropriate EPS bearers in LTE networks. They enable the multiplexing of various traffic flows onto shared bearers and are key to managing quality of service (QoS).
TFTs play a vital role in:
- Mapping incoming data flows to the correct QoS levels and bearers.
- Allowing optimization and prioritization of different services.
- Managing overall user quality of experience.
By intelligently assigning data flows to appropriate dedicated or default bearers, TFTs empower operators to meet demanding performance requirements across various applications. Their filtering and mapping capabilities are essential building blocks for end-to-end QoS management.
How to Make Hotspot Faster on iPhone: Tips and TricksUnderstanding TFT concepts and operations paves the way for better leveraging these tools to deliver robust services over LTE networks. We’ll explore additional facets of TFT usage and integration with EPS network elements in subsequent sections.
What are TFTs?
Traffic Flow Templates (TFTs) are packet filters that play a crucial role in Quality of Service (QoS) management in LTE networks. Here’s a quick rundown of some key aspects of TFTs:
- They act as filters that map various subscriber data flows to appropriate EPS bearers and QoS levels. This allows optimization and prioritization of different services.
- TFTs enable the multiplexing of multiple flows across shared bearers. This allows for efficient utilization of radio resources.
- By mapping flows to certain QoS parameters, TFTs are essential for meeting user expectations and managing quality of experience. Things like latency, reliability, and throughput can be tuned on a per-flow basis.
So in summary, TFTs give operators the tools to classify, prioritize, and manage data flows to align with business needs – a very important capability in today’s networks! Understanding how they work provides great insight into QoS and traffic management in LTE.
How Much Does TikTok Pay You for 1 Million Views? A Comprehensive Guide to Monetizing Your TikTok SuccessWhy are TFTs important?
TFTs are crucial for properly managing quality of service (QoS) in LTE networks. By mapping specific data flows to appropriate QoS bearers, TFTs enable the prioritization and optimization of different services. This is essential for ensuring a good quality of experience for users.
Specifically, TFTs allow the network to classify packets based on parameters like port numbers or packet filters. Video streaming traffic can therefore be mapped to a dedicated bearer with higher priority queueing compared to best-effort web browsing traffic. Without TFTs, it would be impossible to distinguish and appropriately treat these different traffic flows.
By leveraging TFTs, operators can cost-effectively implement service-aware QoS levels. Latency-sensitive applications like VoLTE calling can receive preferential handling, while background sync tasks are relegated to lower priority. This granular flow-based QoS control directly impacts overall user experience on the network.
What Font Do iPhones Use? A General Guide to the Different Fonts Used on iPhonesIn summary, TFTs provide the essential packet inspection and policy capabilities required for end-to-end QoS management. They are integral to delivering optimized services and ensuring good quality of experience in LTE networks. Understanding TFT functionality is therefore critical for any mobile network engineer or operator.
TFT Operations in the EPS
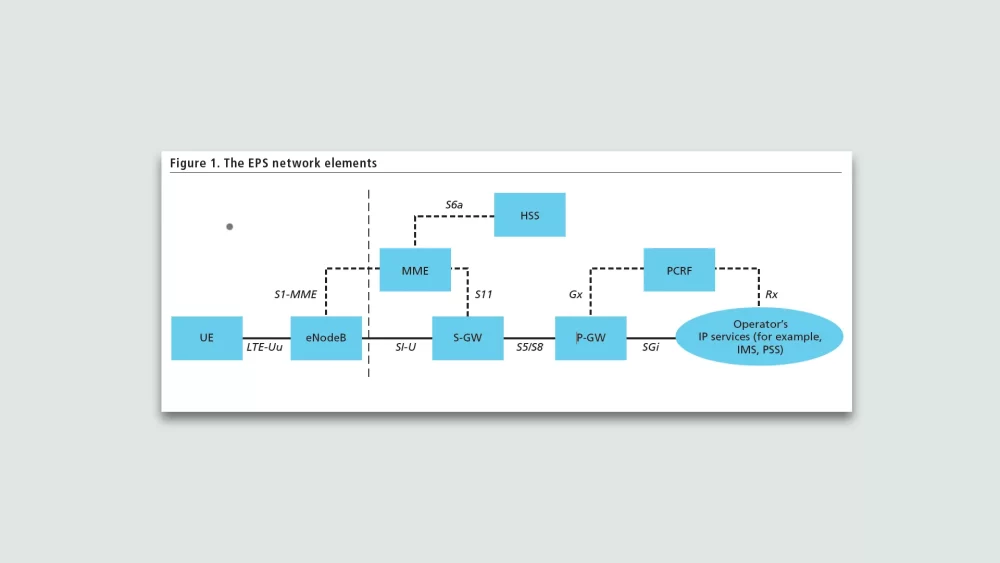
TFTs play an integral role in managing data flows after the initial attach procedure. Once the default bearer is established with a default TFT, the network can add, modify or delete TFTs to optimally map new flows to dedicated EPS bearers.
TFT usage during initial attach
When a UE first attaches to the LTE network, it requests the establishment of a default bearer with an associated TFT. This initial TFT plays a key role in mapping all traffic flows from the UE onto the default bearer.
The Art of Branding: Understanding What Are the 7 Types of Logo Design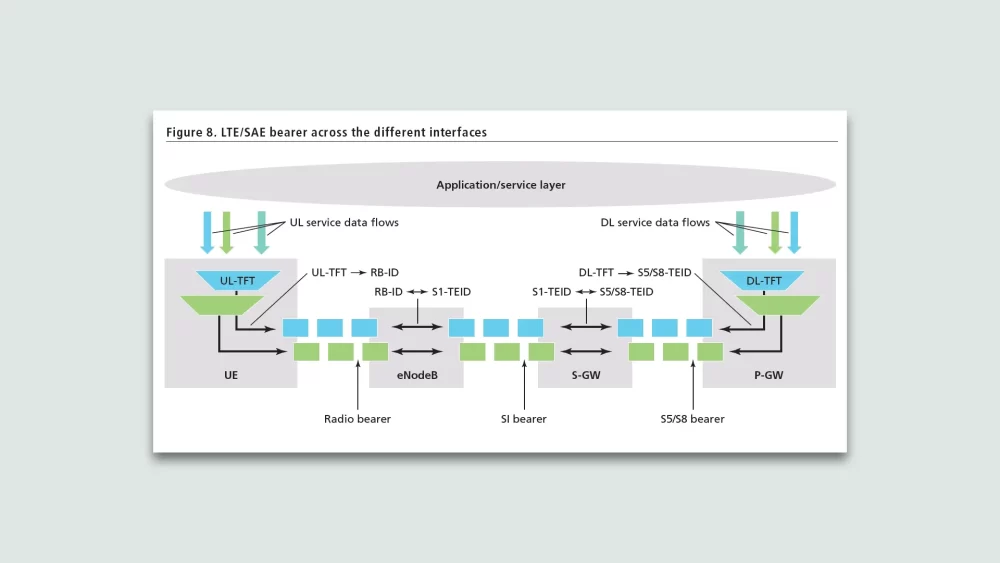
Specifically, during the attach procedure the UE sends a PDN connectivity request that contains the TFT IE (Information Element). This IE specifies packet filters that match all possible traffic flows. So initially, the TFT set by the UE maps any and all traffic to the default bearer created for that PDN connection.
This allows a convenient mapping where all flows can utilize the default bearer QoS parameters. It optimizes the attach procedure by avoiding the need to establish dedicated bearers upfront. Down the line, the network can choose to add, modify or delete TFT filters to map flows onto dedicated bearers to further enhance QoS.
TFT updates after initial attach
After the initial attach procedure establishes the default bearer with a default TFT, the network can update the TFT configuration to better optimize traffic flows. The PCRF and P-GW have the ability to add, modify or delete TFT packet filters on dedicated EPS bearers.
Adding new TFTs facilitates mapping additional QoS flows to new dedicated bearers. Modifying existing TFT filters allows traffic reclassification across bearers. Deleting TFTs can remove unused filters or dedicated bearers.
Performing TFT updates after the initial attach offers more granular control over QoS levels. Specific applications like VoIP, streaming video or online gaming can be assigned to bearers with higher bitrates or lower latency. This enhances the user experience for services with stringent demands.
Overall, the option to dynamically update TFTs is essential to match traffic flows to optimal QoS parameters. This intelligent traffic shaping maximizes utilization of radio and core network resources.
To read the Traffic Flow Template (TFT) blog post, you can simply click on the Understanding the Master Information Block (MIB) link provided.
Key EPS Elements Using TFTs
Serving Gateway (S-GW)
The Serving Gateway (S-GW) serves as the mobility anchor between the eNodeB and PDN Gateway. It transports IP data traffic between the UE and external Packet Data Networks.
The S-GW plays an important role in TFT management within the EPS. It processes TFT signaling and updates TFTs based on instructions from the PCRF. This allows dynamically optimizing QoS configurations for active traffic flows.
UE
The UE (User Equipment) plays an important role in managing TFTs. During the initial attach procedure, the UE requests establishment of a default bearer with an associated TFT. This TFT acts as a packet filter, mapping all traffic flows to the default bearer.
After attach, the UE can request updates to the TFT in order to map additional flows to dedicated bearers with appropriate QoS levels. The UE classifies outgoing IP packets based on the TFT filters and marks them accordingly for proper treatment by the network. So the UE leverages TFTs in order to ensure its various application traffic receives the right QoS treatment.
Proper configuration and handling of TFTs by the UE is essential for end users to obtain the desired quality of experience. The TFT filters enable the prioritization of delay-sensitive services like VoLTE and video calling on dedicated bearers. By classifying flows, the UE plays its part in managing the IP traffic to align with the EPS bearer QoS profiles.
eNodeB
The eNodeB plays a key role in managing TFTs and QoS in the radio access network. It acts as the termination point for all radio-related protocols and handles the scheduling and allocation of radio resources.
Specifically, the eNodeB forwards any TFT signaling messages between the UE and core network components like the Serving Gateway. Whenever a new TFT is created or updated, the eNodeB facilitates this exchange.
Additionally, the eNodeB enforces QoS policies dictated by the TFT mappings. It prioritizes scheduling traffic on radio bearers as specified by the QoS parameters in each TFT. This ensures that services with stricter QoS requirements receive the necessary radio resources and performance.
So while the PCRF and core network do the bulk of TFT policy management, the eNodeB ultimately implements these rules in the radio access network. Its QoS enforcement and handling of TFT signaling makes it an indispensable element in guaranteeing user experience.
Serving Gateway (S-GW)
The Serving Gateway (S-GW) acts as an anchor point between the eNodeB and the PDN Gateway. It serves as a router that manages data traffic flows in the EPS network.
The S-GW has two key functions related to TFTs:
- It acts as an anchor point and traffic router between the radio network (eNodeB) and the PDN Gateway. This allows it to enforce the QoS mappings defined in the TFTs on data flows as they pass through the EPS core network.
- It receives and processes updates to TFTs from the PCRF (Policy and Charging Rules Function). These updates allow the PCRF to dynamically control the QoS parameters for different data flows. The S-GW applies these updated TFT filters to correctly map flows and enforce the updated QoS levels.
So in summary, the S-GW uses the TFT mappings to classify traffic, apply the correct QoS levels, and route flows appropriately between the eNodeB and PDN Gateway. It also handles dynamic TFT updates from the PCRF which helps optimize QoS on an ongoing basis.
Conclusion
In summary, TFTs play a vital role in traffic management and QoS optimization in LTE networks. Understanding key concepts around TFT operations and related EPS elements will help telecom professionals better leverage these tools to map data flows to appropriate QoS levels. This enables the optimization and prioritization of services, which is essential for managing user quality of experience.
The ability to multiplex flows on shared bearers through TFT packet filters is crucial to achieving the necessary granular QoS control in LTE networks. As we saw, TFTs are requested during the initial attach procedure and can be updated afterwards by the network to dynamically manage resources.
By grasping the end-to-end workings of TFTs, from the UE to the core network elements like the eNodeB, S-GW and PCRF, LTE engineers can truly unlock the power of TFTs. This knowledge will prove invaluable for troubleshooting and enhancing quality of service in these complex network environments.
Closing Remarks
I hope this overview gave you a solid high-level understanding of Traffic Flow Templates (TFTs) and their role in LTE networks. We covered what TFTs are, why they’re important for traffic management and Quality of Service, and how they operate within EPS elements like the UE, eNodeB, and Serving Gateway.
TFTs enable optimization of user services by mapping data flows to appropriate QoS levels. They are essential tools for meeting quality of experience expectations. With the key concepts around TFT signaling and usage, telecom professionals can better leverage these mechanisms in LTE deployments.







